The LTO Driver’s License (DL) Codes in the Philippines are crucial for identifying which vehicles a driver is permitted to operate. These codes were used by the Land Transportation Office (LTO) to replace the old driver’s license restriction codes in January 2021 to ensure road safety by matching drivers with vehicles they are trained to handle and to help the authorities enforce traffic laws effectively.
DL Codes represent different vehicle categories and are essential for anyone planning to drive in the Philippines. By understanding these codes, you can ensure you have the correct license for the vehicle you wish to operate, avoiding penalties and promoting road safety. In this guide, we listed all the new DL codes and their equivalent RC codes and vehicle types for your reference.
What Are DL Codes and Restriction Codes (RC)?
Driver’s License Codes (DL Codes) are alphanumeric codes on a driver’s license that indicate the types of vehicles the holder is qualified to operate. These codes ensure that drivers only operate vehicles they are trained and licensed to handle, promoting road safety and compliance with traffic regulations. DL Codes provide specific details about vehicle categories, such as motorcycles, tricycles, passenger cars, and commercial vehicles, along with information about the type of transmission the driver can use.
Restriction Codes (RC) are the previous system of numeric codes serving the same purpose as DL Codes, indicating the vehicle categories a driver can legally operate. While DL Codes are more detailed and specific, RCs offered broader categorization and were simpler in format. The transition from RCs to DL Codes aimed to improve clarity and provide more precise information about the driver’s qualifications and the types of vehicles they are permitted to drive.

DL Codes vs Restriction Codes
While both DL Codes and Restriction Codes are crucial for identifying which vehicles a driver can operate in the Philippines. While they share similarities in purpose, categorization, and transmission information, they differ in designation, format, specificity, and usage. Understanding these distinctions ensures drivers comply with current regulations and only operate vehicles they are qualified to handle.
Similarities
- Purpose: Both DL Codes and RCs specify the vehicle categories a licensed driver is allowed to operate.
- Categorization: Each code classifies vehicles into categories such as motorcycles, tricycles, passenger cars, and commercial vehicles.
- Transmission Types: Both codes include information on whether the driver can operate vehicles with manual transmission (MT) or automatic transmission (AT).
Differences
- Designation:
- DL Codes: The current system used to represent vehicle categories.
- Restriction Codes (RC): The previous system used before the introduction of DL Codes.
- Format:
- DL Codes: Use a combination of letters and numbers (e.g., A, A1, B, C).
- RC: Use numeric values (e.g., 1, 2, 3).
- Specificity:
- DL Codes: More detailed, often specifying subcategories of vehicle types.
- RC: Less detailed, with broader categories.
- Usage:
- DL Codes: Currently in use on new licenses and applications.
- RC: Found on older licenses before the transition to DL Codes.
- Vehicle Category Examples:
- DL Codes:
- A: Motorcycles (e.g., L1, L2, L3)
- A1: Tricycles and four-wheeled vehicles (e.g., L4, L5, L6, L7)
- B: Passenger cars (e.g., M1)
- C: Heavy commercial vehicles (e.g., N2, N3)
- RC:
- 1: Motorcycles and tricycles
- 2 or 4: Passenger cars and light vehicles
- 3 or 5: Heavy vehicles
- DL Codes:
List of DL Codes and their Equivalent Restriction Codes
Understanding the relationship between DL Codes and their equivalent Restriction Codes (RC) is essential for Filipino drivers to ensure they are compliant with current licensing regulations. The transition from RCs to DL Codes has introduced more specific categorizations, improving clarity and safety. Here is a comprehensive list of DL Codes along with their corresponding Restriction Codes.
Motorcycles (DL Code: A)
RC: 1, DL Code: A
Description: Motorcycle
Clutch Code: Manual Transmission (MT) or Automatic Transmission (AT)
Vehicle Categories:
- L1: Two-wheeled, max speed 50 kph
- L2: Three-wheeled, max speed 50 kph
- L3: Two-wheeled, speed over 50 kph

This code allows the operation of motorcycles, including two-wheeled vehicles with a maximum speed of 50 kph (L1), three-wheeled vehicles with a maximum speed of 50 kph (L2), and two-wheeled vehicles exceeding 50 kph (L3). Drivers can handle both manual and automatic transmissions. It ensures that the operator is skilled in managing these types of motorcycles safely.
Tricycles and Four-Wheeled Vehicles (DL Code: A1)
RC: 1, DL Code: A1
Description: Tricycle or TWV
Clutch Code: MT or AT
Vehicle Categories:
- L4: Three-wheeled with sidecar, speed over 50 kph
- L5: Three-wheeled symmetrically arranged, speed over 50 kph
- L6: Four-wheeled, max mass 350kg, speed 45 kph
- L7: Four-wheeled, mass not over 400kg (550kg for goods), speed 45 kph

This code covers tricycles and certain four-wheeled vehicles, such as those with sidecars (L4), symmetrically arranged three-wheelers (L5), and light four-wheeled vehicles with specific speed and weight limits (L6 and L7). It permits driving with either manual or automatic transmissions. The code ensures drivers are qualified to handle various configurations of tricycles and similar vehicles.
Passenger Cars (DL Code: B, B1, B2)
RC: 2 or 4, DL Code: B
Description: Passenger Car
Clutch Code: MT or AT
Vehicle Category:
- M1: Up to 8 seats plus driver, max weight 5000kg
RC: 2 or 4, DL Code: B1
Description: Passenger Van or Jeepney
Clutch Code: MT or AT
Vehicle Category:
- M2: More than 8 seats, max weight 5000kg
RC: 2 or 4, DL Code: B2
Description: Light Commercial Vehicle
Clutch Code: MT or AT
Vehicle Category:
- N1: Goods carriage, max weight 3500kg

DL Codes B, B1, and B2 encompass a range of vehicles from passenger cars to light commercial vehicles. DL Code B covers passenger cars and small utility vehicles with up to 8 seats and a maximum gross vehicle weight of 5000 kg. DL Code B1 permits the operation of larger passenger vans or jeepneys with more than 8 seats and a maximum weight of 5000 kg, while DL Code B2 authorizes the driving of light commercial vehicles used for transporting goods, with a maximum weight of 3500 kg.
Heavy Vehicles (DL Code: C, D, BE, CE)
RC: 3 or 5, DL Code: C
Description: Heavy Commercial Vehicle
Clutch Code: MT or AT
Vehicle Categories:
- N2: Goods carriage, weight 3500-12000kg
- N3: Goods carriage, weight over 12000kg
RC: 3 or 5, DL Code: D
Description: Passenger Bus
Clutch Code: MT or AT
Vehicle Category:
- M3: More than 8 seats, weight over 5000kg
RC: 6, 7, 8, DL Code: BE, CE
Description: Light and Heavy Articulated Vehicles (Trailers)
Clutch Code: MT or AT
Vehicle Categories:
- O1: Trailers, weight not over 750kg
- O2: Trailers, weight 750-3500kg
- O3: Trailers, weight 3500-10000kg
- O4: Trailers, weight over 10000kg
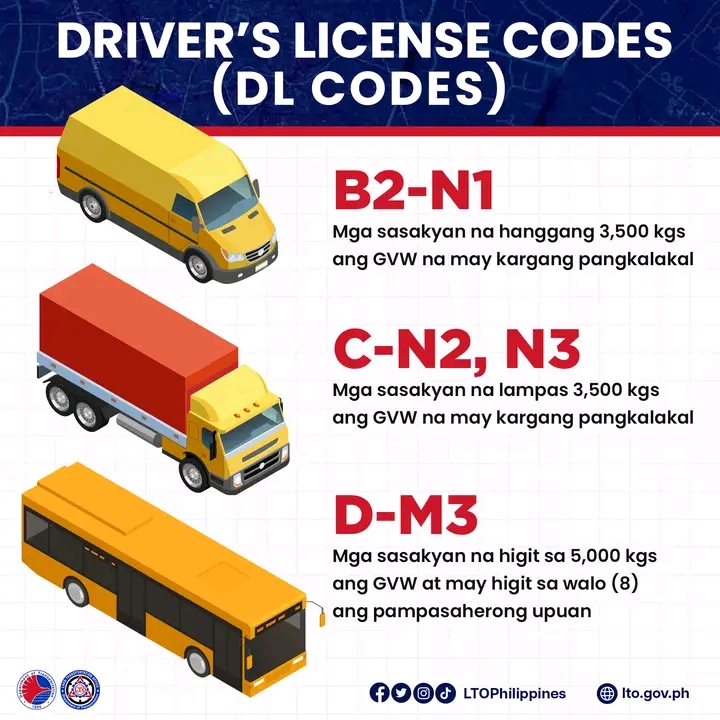
DL Codes C, D, BE, and CE cater to heavy commercial and articulated vehicles, ensuring drivers are qualified for more demanding driving tasks. DL Code C permits the operation of heavy commercial vehicles, including trucks with a gross vehicle weight exceeding 3500 kg. DL Code D allows drivers to handle large passenger buses with more than 8 seats and a gross vehicle weight over 5000 kg, while DL Codes BE and CE cover light and heavy articulated vehicles, respectively, including various types of trailers with gross vehicle weights ranging from 750 kg to over 10000 kg.
The DL codes listed above categorize and specify the types of vehicles Filipino drivers are licensed to operate. These codes reflect specific vehicle categories and transmission types, ensuring drivers’ qualifications align with the vehicles they can safely drive on Philippine roads.
How to Read LTO Driver’s License Codes
The codes on your license include three components: vehicle category, license classification, and transmission/clutch type.
- Vehicle Category: Indicates the types of vehicles you can operate (e.g., L1 for motorcycles, M1 for passenger cars).
- License Classification: Shows if the license is professional (PL) or non-professional (NP).
- Transmission/Clutch: MT for manual, AT for automatic. MT allows operating both types, while AT limits to automatic only.
Examples
Some examples include:
N1 – PL – MT
Vehicle Category: N1 (Light Commercial Vehicles)
License Classification: Professional
Transmission/Clutch: Manual Transmission
M1 – PL – AT
Vehicle Category: M1 (Passenger Cars)
License Classification: Professional
Transmission/Clutch: Automatic Transmission
L4, L5, L6, L7 – PL – MT
Vehicle Categories: L4 to L7 (Tricycles and Four-Wheeled Vehicles)
License Classification: Professional
Transmission/Clutch: Manual Transmission
Video: LTO DL Codes Meaning and Purpose
Learn everything you need to know as Jeff Ski delves into the intricacies of the LTO DL Codes and their equivalent Restriction Codes (RC) via this comprehensive video overview of these codes. It also details how the new DL codes categorize the different vehicle types and how it compares with the old restriction codes along with the vehicles you can legally operate for each type.
Summary
The LTO Driver’s License (DL) Codes replaced the Driver’s License Restriction Codes (RC) in the driver’s license issued by the LTO in January 2021 to indicate which vehicles you are qualified to operate, whether your license is professional or non-professional, and the type of transmission you can handle. Being familiar with these details helps ensure compliance with traffic regulations and operate vehicles safely. Though similar in purpose, the DL codes offer a more inclusive and more detailed designation pertaining to the vehicle type each driver is allowed to operate.