LTO Driver’s License codes (DL codes) and condition codes are systems developed by the Land Transportation Office (LTO) to classify the types of vehicles a driver is permitted to operate and to indicate any specific driving restrictions based on medical or physical conditions. Originally, the LTO used numerical restriction codes (RC Codes), but these evolved into a more detailed alphanumeric system—known as DL codes—in 2021 to provide greater clarity and precision. This evolution reflects the background and rationale of enhancing road safety by ensuring drivers are matched to vehicles they are adequately equipped to handle.
The DL codes cover a broad spectrum of vehicle categories—from motorcycles and cars to heavy trucks and trailers—while condition codes detail requirements like corrective lenses or special equipment for limb impairments. Understanding these codes is important because they not only help enforce road safety regulations but also protect drivers from unknowingly operating vehicles beyond their capability. Being aware of your specific DL and condition codes enables you to verify your driving privileges, comply with legal standards, and make informed choices about the vehicles you drive. In this guide, we break down the different license classifications, describe the vehicle categories with sample vehicles, and explain the associated medical condition codes along with their restrictions.
LTO Restriction Codes (RC) vs LTO DL Codes
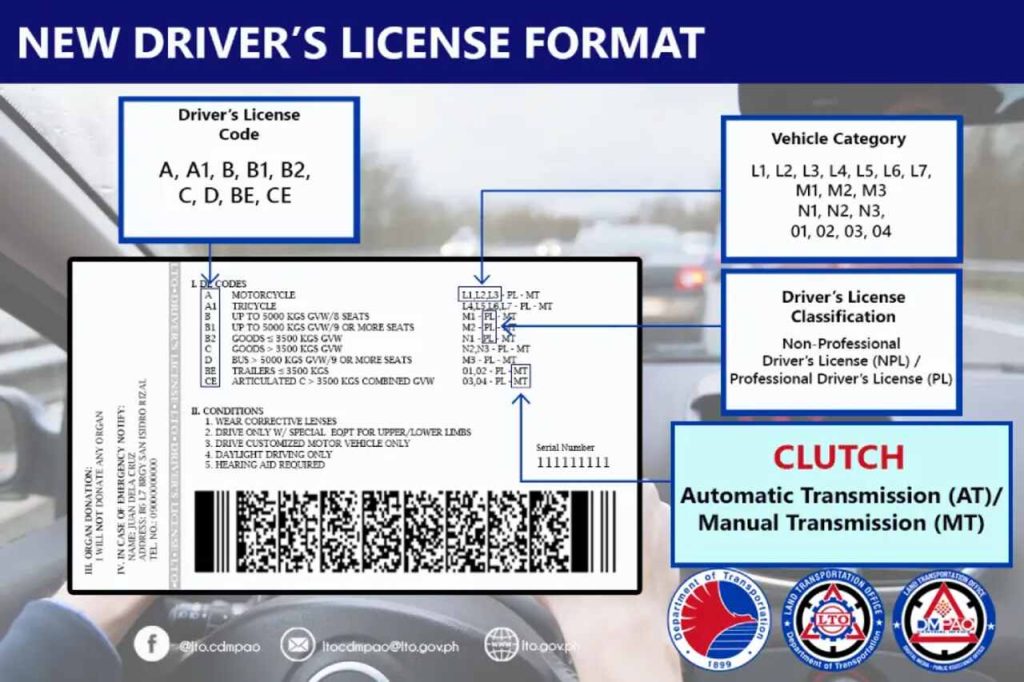
While both the LTO RC and DL codes define the parameters under which drivers can operate various vehicles, outlining any limitations that may apply. The older codes which used numbers primarily identified specific physical or medical limitations, while the modern alphanumeric DL codes combine these both limitations or adaptations required for safe driving with detailed vehicle classifications. The current DL codes also incorporate vehicle design standards and updated safety measures, making them a more comprehensive system than the old RC approach. They provide clearer distinctions between categories and what each category covers such as the type, design, weight, and configuration of vehicles. It also clearly differentiate between motorcycles, passenger cars, commercial trucks, and trailers, which simplifies the licensing process. Overall, DL codes offer a more precise and user-friendly method for matching drivers to the appropriate vehicle types and their corresponding restrictions.
List of LTO DL Codes
To better understand what these DL codes are and what they mean, here’s a quick guide for you:
LTO DL Codes for Two-Wheeled and Related Vehicles
Code A: Two-Wheeled and Three-Wheeled Vehicles
DL Code A – L1, L2, and L3
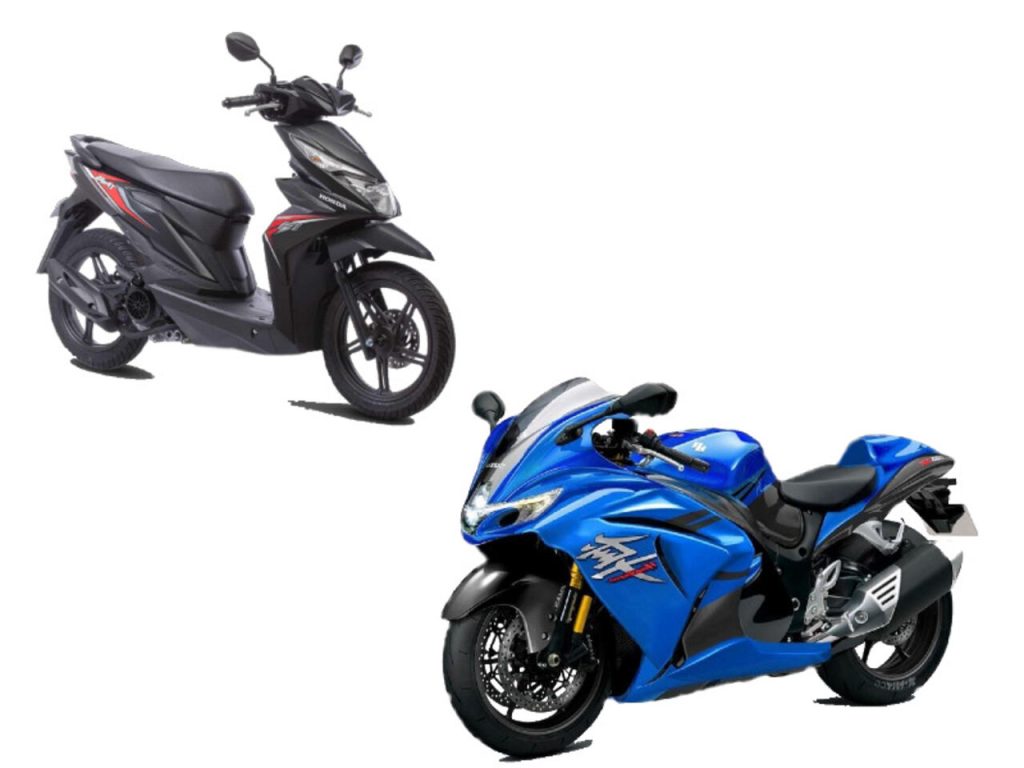

- L1: This designation applies to standard two-wheeled vehicles with a maximum design speed not exceeding 50 kilometers per hour. Typical examples include common motorcycles, such as commuter bikes or low-powered scooters, available in both manual and automatic transmission.
- L2: Under this classification, the code is used for three-wheeled vehicles that also have a maximum design speed of 50 kph or less. An example might be a low-speed auto-rickshaw or similar personal transport vehicle that provides an alternative to the standard motorcycle.
- L3: This classification refers to two-wheeled vehicles capable of speeds exceeding 50 kph. These include higher-performance motorcycles, such as sports bikes, which are engineered for speed and agility.
DL Code A1 – L4
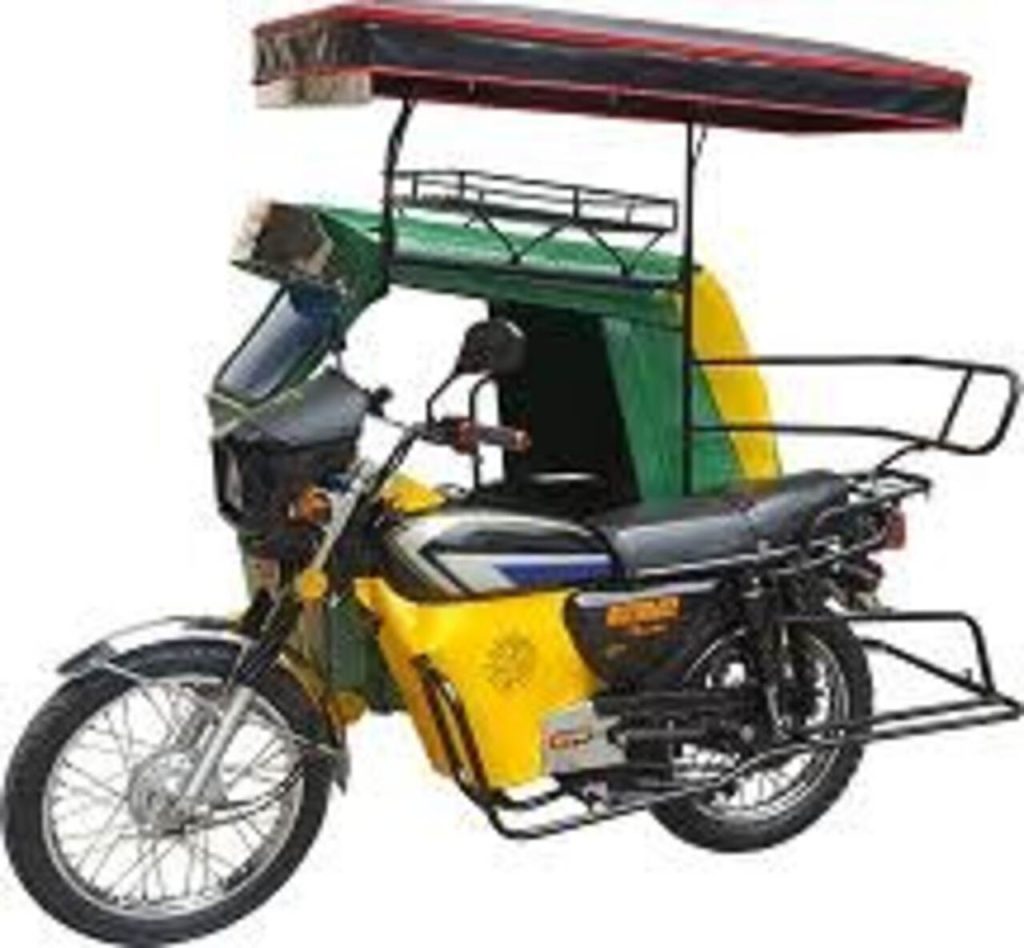

- L4: Vehicles under this code feature three wheels arranged asymmetrically. In other words, this category covers motorcycles with sidecars, typically designed to achieve speeds above 50 kph. Many riders who require additional seating or extra storage opt for these vehicles, which are a distinctive variation of the traditional motorcycle.
Code A Variants for Unique Three- and Four-Wheeled Vehicles
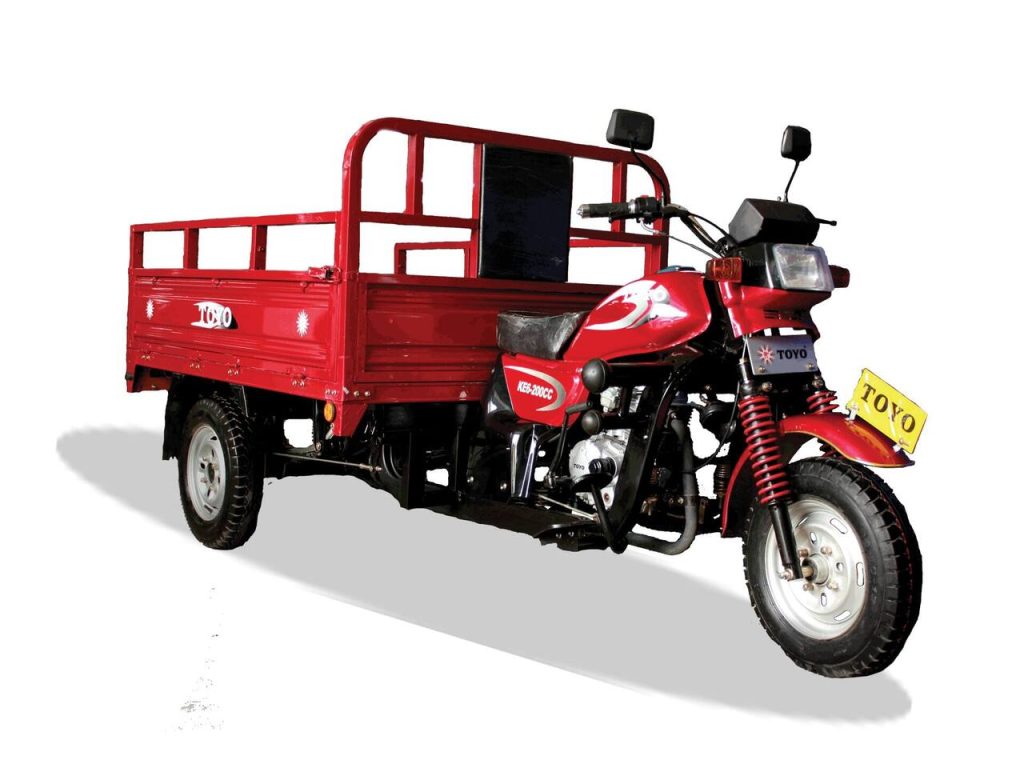

- L5: This code is designated for vehicles with three wheels that are symmetrically arranged in relation to the vehicle’s center line. These vehicles may be seen in modern three-wheeled designs that offer better stability compared to their asymmetrical counterparts. A sample might be a specially designed three-wheeled urban vehicle, sometimes used for delivery or light transport services.
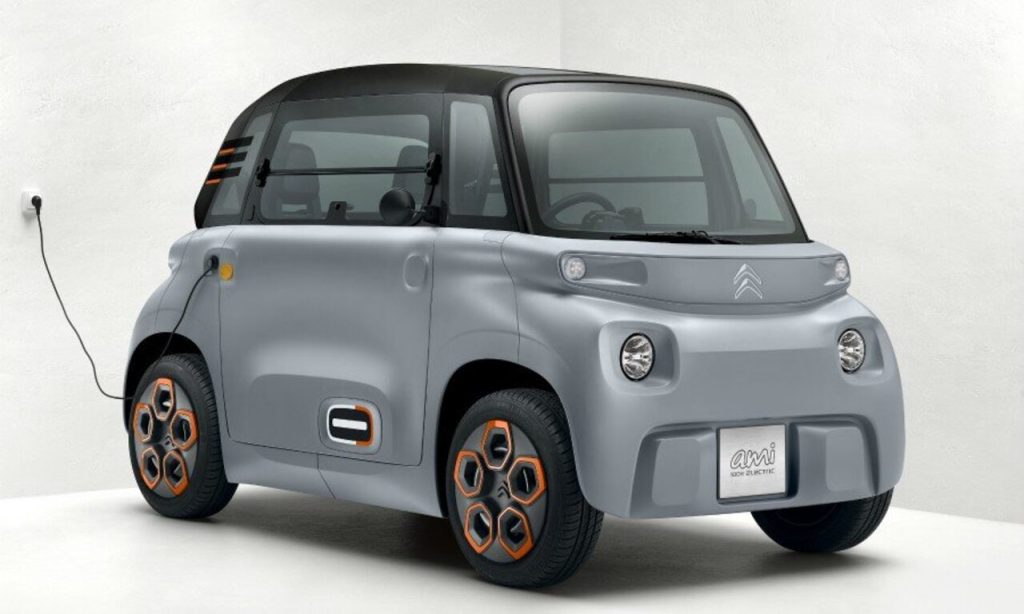

- L6: L6 applies to a specific group of four-wheeled vehicles that have an unladen mass not exceeding 350 kilograms (excluding batteries for electric vehicles) and a maximum design speed of up to 45 kph. Examples include compact quadricycles or microcars that are engineered for short distances in urban settings.
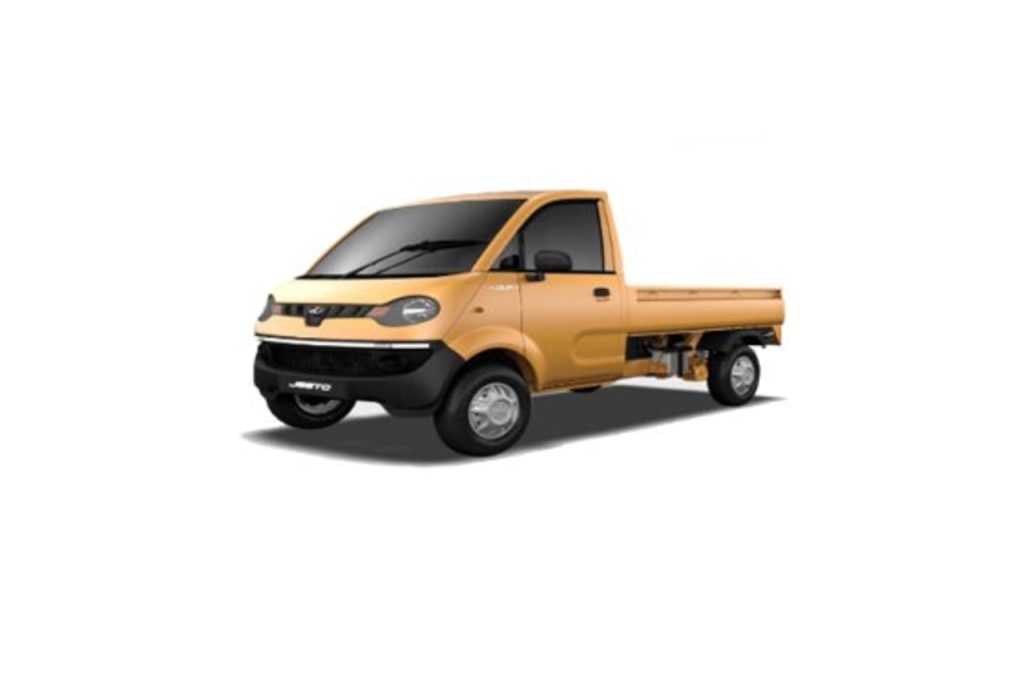

- L7: This category covers slightly heavier four-wheeled vehicles that are not classified under L6. With an unladen mass not exceeding 400 kilograms (or 550 kilograms for vehicles intended for carrying goods) and a design speed capped at 45 kph, vehicles in this group often include lightweight utility vehicles, which are common in local delivery and service industries.
LTO DL Codes for Passenger and Commercial Vehicles
Code B Series: Passenger and Goods-Carrying Vehicles
DL Code B (M1)
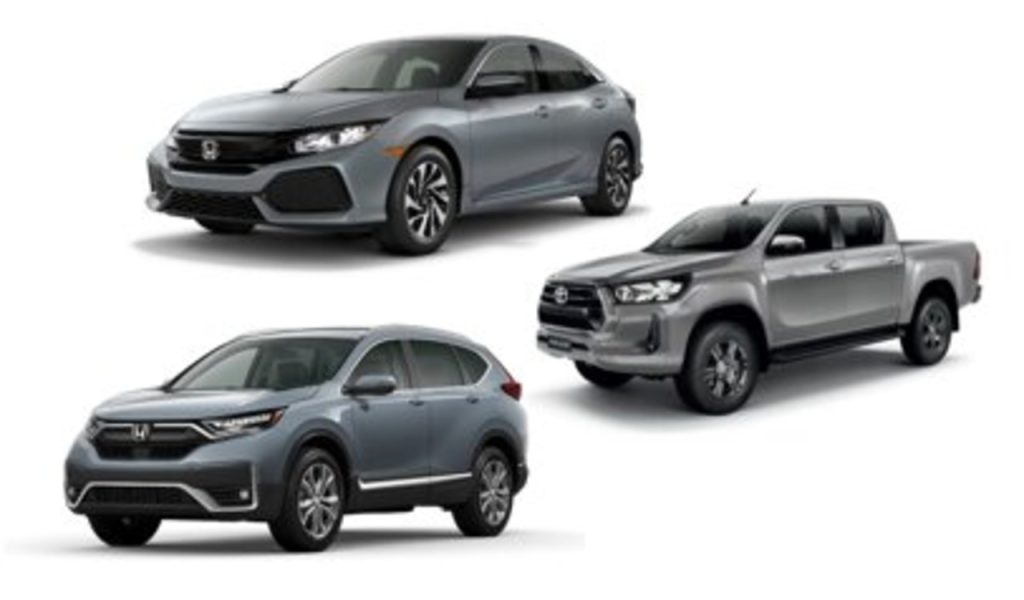

- M1: This classification is for vehicles used primarily for transporting passengers. It applies to vehicles that have no more than eight passenger seats, in addition to the driver’s seat, and a gross vehicle weight (GVW) of up to 5000 kilograms. Common sample vehicles include everyday passenger cars, sedans, compact SUVs, and hatchbacks that cater to personal and family transportation needs.
DL Code B1 (M2)

- M2: This code is reserved for larger passenger vehicles that carry more than eight passengers, excluding the driver, while still maintaining a GVW of up to 5000 kilograms. Examples include minibuses or larger vans, which are often utilized in group transport services or by small public utility providers.
DL Code B2 (N1)

- N1: Under this classification, the focus shifts to vehicles built for carrying goods. These vehicles have a maximum gross vehicle weight of up to 3500 kilograms and typically include small delivery trucks and light commercial vehicles, ideal for urban cargo transport and distribution.
LTO DL Codes for Heavier Vehicles and Trailers
Code C and D: Heavy Goods and Passenger Transport
DL Code C (N2)

- N2: Vehicles classified under this code are designed for the carriage of goods, with a GVW exceeding 3500 kilograms but not surpassing 12000 kilograms. Medium-sized trucks, which are often used for regional distribution and logistics, serve as typical examples in this category.
DL Code C (N3)
- N3: This designation is for goods-carrying vehicles that weigh more than 12000 kilograms. These heavy-duty trucks are used extensively in long-haul freight and industrial transportation, making them a common sight on highways connecting major commercial hubs.
DL Code D (M3)

- M3: The focus here is on vehicles used for transporting a large number of passengers, specifically those with more than eight seats in addition to the driver’s seat and a GVW exceeding 5000 kilograms. Buses fall under this category—ranging from city transit buses to tour buses that are designed to accommodate large groups of people.
Trailer Classifications
Trailers are also grouped into separate codes based on their weight limits and intended usage:

- BE (O1): Trailers under this code have a maximum GVW of up to 750 kilograms. They are typically small utility trailers that might be used for transporting light loads in residential or small business settings.
- O2: This classification covers trailers with a GVW that exceeds 750 kilograms but does not exceed 3500 kilograms. Such trailers are commonly seen in commercial applications, serving as mid-sized trailers for various types of cargo.

- CE (O3): For larger transport needs, this code applies to trailers weighing more than 3500 kilograms but not more than 10000 kilograms. Examples include trailers used in larger commercial transport fleets.
- O4: Finally, trailers with a GVW that exceeds 10000 kilograms fall under this category. These heavy-duty trailers are built for industrial use and are often paired with specialized tractor units for long-distance freight hauling.
Medical Condition Codes and Driving Restrictions
Apart from vehicle classifications, the LTO also assigns medical condition codes to highlight any physical or sensory limitations that might affect a driver’s performance. These codes come with specific driving restrictions designed to maintain safety on the road.
Medical Condition Code 1: Corrective Lenses
Drivers with this code must operate their vehicle only while wearing corrective lenses, such as glasses or contact lenses. This restriction is applied to those whose vision does not meet the minimum standard unless corrected. Whether you drive a motorcycle, car, or truck, having proper vision is key to safe driving.
Medical Condition Code 2: Special Equipment for Limbs
This code indicates that the driver requires vehicles equipped with special equipment for either the upper limbs or lower limbs. Such modifications may include hand controls or pedal extensions, allowing drivers with limb impairments to maneuver the vehicle effectively.
Medical Condition Code 3: Customized Vehicles Only
Drivers assigned this code are restricted to operating vehicles that have been specifically modified to accommodate their physical condition. Customized vehicles might feature adapted controls, adjusted seating arrangements, or other modifications that facilitate safe operation despite physical limitations.
Medical Condition Code 4: Daylight Driving Only
This restriction applies to drivers who are permitted to drive only during daylight hours. Often, this code is given to individuals with certain visual impairments—such as partial blindness in one eye—where night driving poses significant risks.
Medical Condition Code 5: Driving with a Hearing Aid
Drivers with hearing impairments receive this code, which mandates that they must drive only with the use of a hearing aid. This precaution helps in maintaining auditory awareness while operating a vehicle, whether it is a small car or a heavy truck.
It is important to note that individuals with Medical Condition Codes 2, 3, 4, or 5 are generally restricted from driving For-Hire, Public Utility Vehicles (PUVs), or any commercial vehicles unless a qualified medical specialist provides written permission. These added measures help to reduce the likelihood of accidents while accommodating specific physical limitations.
Video: DL Codes and Their Meanings
The LTO’s system of DL codes and medical condition codes provides a structured framework that matches drivers with the vehicles they are certified to operate. The classifications range from two-wheeled motorcycles and modified vehicles to passenger cars, heavy trucks, and trailers. Additionally, the LTO’s medical condition codes offer guidelines on specific driving restrictions. Additional permissions are also needed for those with certain conditions to operate commercial vehicles, reflecting the comprehensive approach taken by the LTO to maintain road safety. For any driver in the Philippines, familiarity with these license classifications and medical condition codes is a significant step toward complying with LTO regulations. Watching this video from Philippine Assistance will help you do just that.